The DHT-11 is a temperature and humidity sensor that use only one bidirectional serial data pin. The converted temperature is between 0 and 50 degree Celsius. Its working humidity is between 20 and 90 RH.
 |
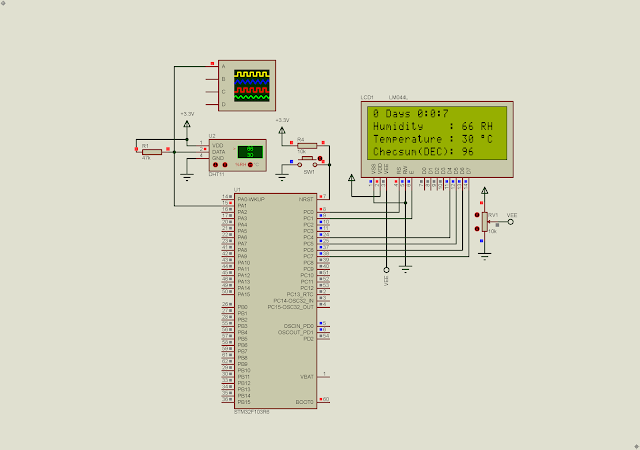
| Program Simulation in Proteus |
The sensor data is very easy to decode using only ones microprocessor digital pin. I don't show the details of serial data transmission here. You can see the post that use a PIC1F84A to decode the signal.
 |
| DHT-11 Humidity & Temperature Sensor |
We can get this sensor at local electronics parts store around 1USD. In this example, I use the STM32F103R6 to read environmental data from this sensor. The temperature and humidity will show on a 20x4 character LCD.
Click here to download its source file.